Crypto Mainnet vs Testnet: What is the Difference?
This article takes a look at what is the difference between a crypto mainnet vs testnet, two technical terms that serve different functions.
Mainnets and testnets are common technical terms used in the cryptocurrency world to denote blockchain networks that possess vital functions. Let’s take a look at the differences between a cryptocurrency mainnet and testnet:
What is a Mainnet?
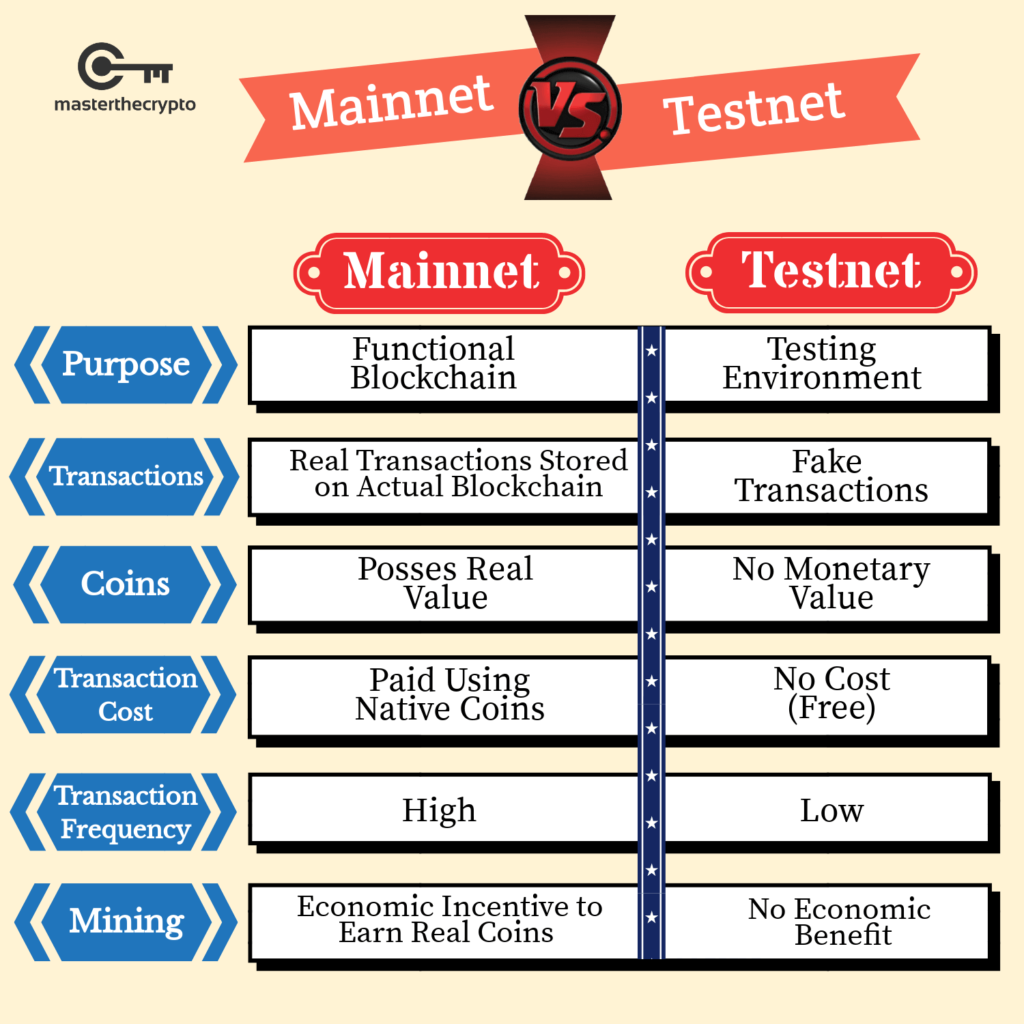
Mainnet – short for main network – is the original and functional blockchain where actual transactions take place in the distributed ledger and the native cryptocurrencies possess real economic value. In other words, the mainnet refers to the actual open-sourced blockchain itself that is publicly verifiable. The mainnet carries out the functionality of executing real transactions within the network which is stored on the blockchain and is referred to as the ‘end product’ that is open for the public to use.
Each transaction executed on the blockchain requires participants to pay a transaction fee (payable in the native coin) so as to incentivize miners to validate the transactions and prevent network spamming. For their hard work, miners will be rewarded with native coins from the protocol and also the transaction fees paid by the participants.
(Read more: Coins, Tokens & Altcoins: What’s the Difference?)
Importance of Mainnet
A mainnet serves a variety of vital functions that include:
1) Proof of Development
A Mainnet is a verifiable proof that the project has developed a functional and working blockchain where actual transactions can take place. Having a mainnet is a sign that the project is now live and is in technical progress. Additionally, a live mainnet would put the functionalities and capabilities of the blockchain to the test, since the public can participate in the network and any malfunction could compromise the inner workings of the blockchain. Therefore, launching the mainnet takes a considerable amount of resources and development to ensure that every component is working as it should. More than that, a mainnet serves as a working proof that the project is executing their vision well.
2) Credibility
A project with a mainnet possesses undoubtedly more credibility than a project without one. Since a mainnet is an actual and functioning protocol, all transactions are live and participants can transact with one another with the native coins of the blockchain. interested parties in the community can opt to become a participating node and download the protocol software. Assuming that the blockchain is open-sourced and free for anyone to participate in, the underlying codes of the blockchain is visible to the public and any concerns or issues can be highlighted by participants. The point is, the existence of a mainnet enables the creation of a live ecosystem of participants that facilitates real interaction and transactions to occur with full transparency. Without a mainnet, the project is purely conceptual or ‘theoretical’ with no working product for participants to test out. This is particularly important to understand when evaluating an ICO project that is trying to raise money; it is much harder to evaluate projects without a mainnet or even a testnet.
(See more: A Guide To Fundamental Analysis For Cryptocurrencies)
What is a Testnet?
The testnet- short for test network – is an exact replica of the original blockchain, with the same technology, software, and functionalities. The only difference is that transactions on the testnet are simulated (or ‘fake’) and the coins in the testnet does not possess any real value outside of the testnet environment.
The native coins in a testnet are like monopoly money. You can’t buy anything with that.
The testnet is a simulated environment where the functionalities and capabilities of the (original) blockchain are constantly tested and tweaked by application developers and testers. The purpose of having a mainnet is to develop the blockchain before it goes live or for ongoing testing of blockchain functionalities in a sandbox environment that is separate from the actual blockchain. The transactions on the mainnet are ‘fake’ since they are test transactions, with no transaction costs incurred and no deployment costs required by developers. Since the coins on the testnet are worthless, there is no economic incentive for miners to mine since their only purpose is to facilitate transaction testing.
In summary, activities deployed on the mainnet serves as a simulation of how the protocol would function on the mainnet itself.
Just like how pilots need to undertake 3D-simulation of flying planes before flying an actual plane, a testnet provides a testing ground for developers to test the protocol’s functionalities.
(Read also: Is it Too Late to Buy Bitcoin and Is It too Late to Invest in Cryptocurrency?)
Importance of Testnet
Testnet serves a variety of vital functions that include:
1) Constant Development
Blockchain technology is still in the infancy stages and a tremendous amount of testing and development is needed to enable mainstream adoption and usage. For instance, one of the main issues that are being addressed in the blockchain community is scalability. Rigorous research and development are being undertaken by a wide range of projects to enhance a blockchain’s capability of processing more transactions. In order to constantly enhance a blockchain’s capabilities, numerous testing on smart contract functionality, transactions, and the mining process must be undertaken. The testnet serves as a simulation on how the actual blockchain protocol (mainnet) would work under real-world conditions.
2) Prevent Disruption
A testnet allows testers and application developers to experiment on the features and functions of the protocol in a separate environment, without worrying about disrupting the main blockchain. Making the tests on the mainnet would be a nightmare since the complex interactions between components in the protocol could compromise the network or break the main chain. This would cause massive disruptions to the blockchain and could undermine the protocol. It is thus a common practice for projects to run a prototype on a testnet first, in order to iron out the technical details and ensure that everything is in order.
3) Free Testing
For blockchains that allow smart contract functionality, native coins are required to be spent in order to execute smart contract transactions. For instance, Ether (ETH) is needed to pay for computations that occur in the Ethereum blockchain (Similarly called ‘Ethereum Virtual Machine’). Testnets provide a testing ground for developers who are keen to create applications on the blockchain or test out certain functionalities without spending real currencies. It would be extremely expensive for developers to test out their application features or run experiments on the mainnet, since they would then need to buy real-value coins in bulk.
(See also: Public Vs Private Blockchain: What’s The Difference?)
Mainnet vs Testnet in Action
In order to get a better grasp of the differences between mainnet and testnet, let us take a look at Ethereum blockchain. Ethereum is an open-source, decentralized platform that facilitates smart contract functionality and allows for the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) to run securely without any control from intermediaries or third party.
Think of Bitcoin as a single app in your smartphone that is great in what it does, which is to facilitate value efficiently (digital cash). Ethereum on the other hand is like the app store, which enables anyone to create any kind of mobile applications and can be downloaded and used by anyone. Blockchain platforms like Ethereum expand the functionality of blockchain technology, while Bitcoin is just a single representation of this revolutionary technology.
A mainnet and a testnet are two separate networks that operate independently from each other. Here’s an illustration from the context of Ethereum:

Ropsten is the most popular public testnet for Ethereum and is often used as a testing network for developers creating their own dApps on the Ethereum blockchain. Using Ropsten network, DApp developers can experiment on the functionalities on the dApp and also avoid using valuable ETH that is needed for transaction fees and smart contract deployment. Once they’re confident that their dApps work and testing is complete, they can confidently deploy their dApp on the main Ethereum network!
What sets a mainnet and testnet apart are the following factors:
- Network ID: A network ID is just an identifier for a network, similar to your ID card that represents your identity. If a new node wants to join the actual Ethereum blockchain itself), they will need to join the mainnet which has a network ID of 1. If they’re keen on joining the testnet instead, they can join the Ropsten testnet which is identified using a network ID of 3.
- Genesis Block: This refers to the very first block in the blockchain, which represents the starting point. Since both the mainnet and tesnet are different networks, they have a different genesis block. However, the content of the genesis block can be similar.
(Read more: Guide to Ethereum: What is Gas, Gas Limit and Gas Price?)
Upgrades
From time to time, projects would undergo changes to enhance the capabilities of the blockchain. This is akin to the software updates of your smartphones that has solved previous issues or bugs associated with the previous software versions. Although we mentioned early on that mainnets are the ‘end product’, it may not be the ‘final product’. The blockchain can undergo updates or revisions to a particular functionality, depending on the need of doing so by the developers and the greater community. In order to upgrade the blockchain, a hardfork is required. Here is a detailed guide that explains the complex concept of hard forks.
(See more: Guide to Forks: Everything You Need to Know About Forks, Hard Fork and Soft Fork)
Mainnet Swap
When a project is starting out, it will issue their tokens on other blockchains such as Ethereum or NEO to raise funds. Once they have developed their own blockchain, they will need to migrate the existing tokens issued on other blockchains to the project’s native blockchain (mainnet). This is common practice for new projects in the ICO phase.
This process is called a mainnet swap or a token swap, involving the exchange of one coin for another coin on a one-to-one ratio. The old coin that is issued on another blockchain is discarded and a new coin is issued on the new native blockchain that has been developed and launched by the project. Mainnet swaps usually occur in the following way:
- Registration & Auditing: Coin holders are expected to register their coin through the project’s developers, who will then accredit these coins through a supported digital wallet. At the scheduled mainnet swap date, the old tokens are burned while the new, official coins will replace the old coins in the same wallet.
- Cryptocurrency Exchange Support: Once the announcement is made, coin holders are invited to keep their coins in the cryptocurrency exchange that supports the swapping process. At the scheduled swap date, the exchange will handle the auditing, accrediting and exchange of the older coin for the newer ones.
(Read also: Breaking: 88% of Crypto Exchanges are Manipulating Trading Volume to ‘Boost’ Rankings)
Effects of Mainnet on Price
The release of a project’s mainnet can cause tremendous excitement in the community, which could affect the coin’s price. This could also contribute to an increase in volatility of the coin’s prices during that period. Let’s take a look at several instances where a mainnet launch coincided with spikes in prices.
Golem (GNT)

Golem is a project that is focused on creating a decentralized marketplace for sharing computing power. They released their mainnet – called Brass – on April 2018. Here’s a look at how prices reacted to the launch of the mainnet.

Golem announced on mid-February that their mainnet would be ready by the end of March to early April. The duration leading up to the mainnet launch saw GNT’s prices consolidating with relatively low volatility, as indicated by a technical analysis indicator called the Relative Volatility Index (RVI) at the bottom of the chart. When Golem officially launched their mainnet on April 10, prices started to soar tremendously, going from $0.20 to $0.60 within a span of 3 days. That’s a three-fold increase in prices! We can also see that there is an increase in volatility after the mainnet launch, which means that there is an increase in risk during that period.
(See also: 4 Types of Coins to Diversify Your Crypto Portfolio & Manage Risks)
Tron (TRX)

Tron is a blockchain platform focused on creating a decentralized entertainment ecosystem. It’s mainnet – called Odyssey 2.0 – was officially launched on June 1. Let’s see how it affected prices:

The announcement for the release of Tron’s mainnet was made on April 9, which saw TRX’s prices increase from $0.035 to $0.1 within 2 weeks. That’s a solid 3-fold increase in prices. This pump in prices is also caused by Tron’s announcement of distributing an airdrop of over $1.7 million on April 21, as a show of gratitude to their token holders. However, the hype generated by Tron was too great and led to a price decline a month before the actual release of their mainnet. In fact, prices continued to move downhill even after the official mainnet release, with no apparent fundamental reason that substantiates an increase or a decrease. We can imply that the hype around Tron’s mainnet was purely fuelled by sentiments.
A mainnet launch is one of the many factors that may affect the value of a cryptocurrency since its launch represents a successful start by the developers in delivering the promises set in their project roadmap. From then on, the team is expected to drive the project development forward through continual enhancement and upgrading. Although a mainnet is an essential technical aspect to consider when investing in a project, it is not unusual for the absence of mainnets or testnets in cryptocurrency projects, especially if they’re starting out and are in the ICO stages. However, rigorous due diligence has to be done in order to assess the quality and viability of the project. From our examples in Golem and Tron, it is not substantive that mainnet launches have a positive or negative impact on prices since it is largely based on the context behind the projects.
(See more: Bitcoin vs Alt Coins Returns: Comparison of Gains Between Bitcoin & Altcoins Investing)
All in All
Mainnets and testnets represent two fundamentally different networks that each represent a vital purpose for any project. A testnet is often used as a testing site for the development and continual enhancement of the mainnet, while the mainnet itself is the actual, functioning protocol that powers the blockchain network. It is important for any investor to evaluate a project based on the success of both their testnets and mainnets, since they represent a good proxy for the technical development of the project’s vision.
(You should also read: Guide to Market Capitalization: Everything You Need to Know About Market Cap)
Beneficial Resources To Get You Started
If you’re starting your journey into the complex world of cryptocurrencies, here’s a list of useful resources and guides that will get you on your way:

Trading & Exchange
- Crypto Guide 101: Choosing The Best Cryptocurrency Exchange
- Guide to Bittrex Exchange: How to Trade on Bittrex
- Guide to Binance Exchange: How to Open Binance Account and What You Should Know
- Guide to Etherdelta Exchange: How to Trade on Etherdelta
- Guide To Cryptocurrency Trading Basics: Introduction to Crypto Technical Analysis
- Cryptocurrency Trading: Understanding Cryptocurrency Trading Pairs & How it Works
- Crypto Trading Guide: 4 Common Pitfalls Every Crypto Trader Will Experience
Wallets
- Guide to Cryptocurrency Wallets: Why Do You Need Wallets?
- Guide to Cryptocurrency Wallets: Opening a Bitcoin Wallet
- Guide to Cryptocurrency Wallets: Opening a MyEtherWallet (MEW)
Read also: Crypto Trading Guide: 4 Common Pitfalls Every Crypto Trader Will Experience and Guide To Cryptocurrency Trading Basics: Introduction to Crypto Technical Analysis.
Sponsored Ad: Your dog deserves to be healthy & happy
Enroll in our Free Cryptocurrency Webinar now to learn everything you need to know about crypto investing.
Get our exclusive e-book which will guide you on the step-by-step process to get started with making money via Cryptocurrency investments!
You can also join our Facebook group at Master The Crypto: Advanced Cryptocurrency Knowledge to ask any questions regarding cryptocurrencies.

I’m Aziz, a seasoned cryptocurrency trader who’s really passionate about 2 things; #1) the awesome-revolutionary blockchain technology underlying crypto and #2) helping make bitcoin great ‘again’!
The post Crypto Mainnet vs Testnet: What is the Difference? appeared first on Master The Crypto.